The nettle ecosystem
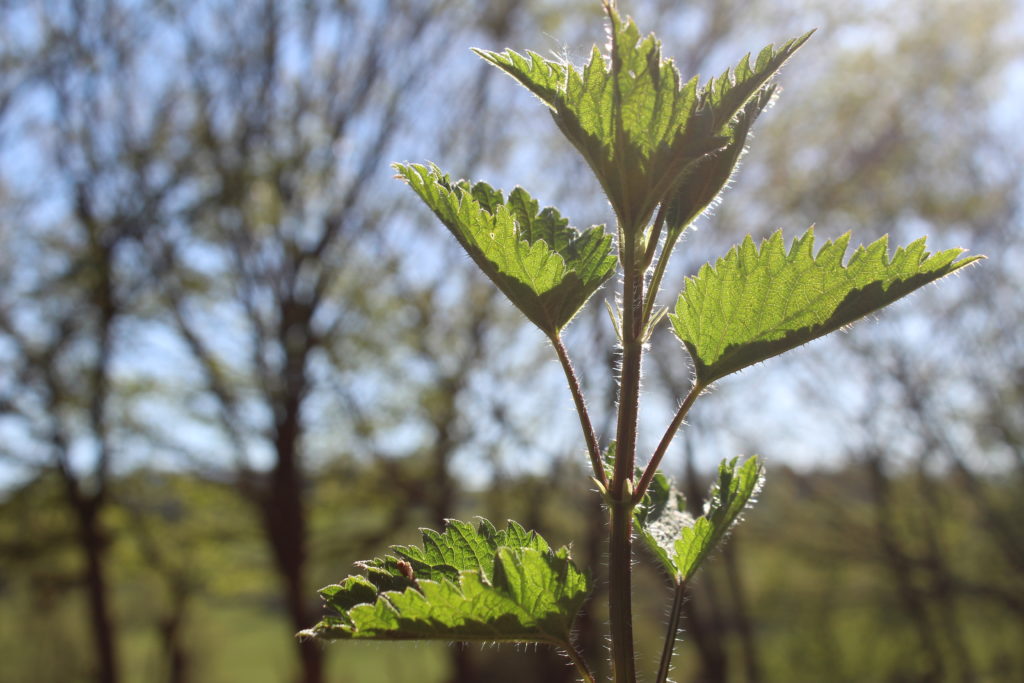

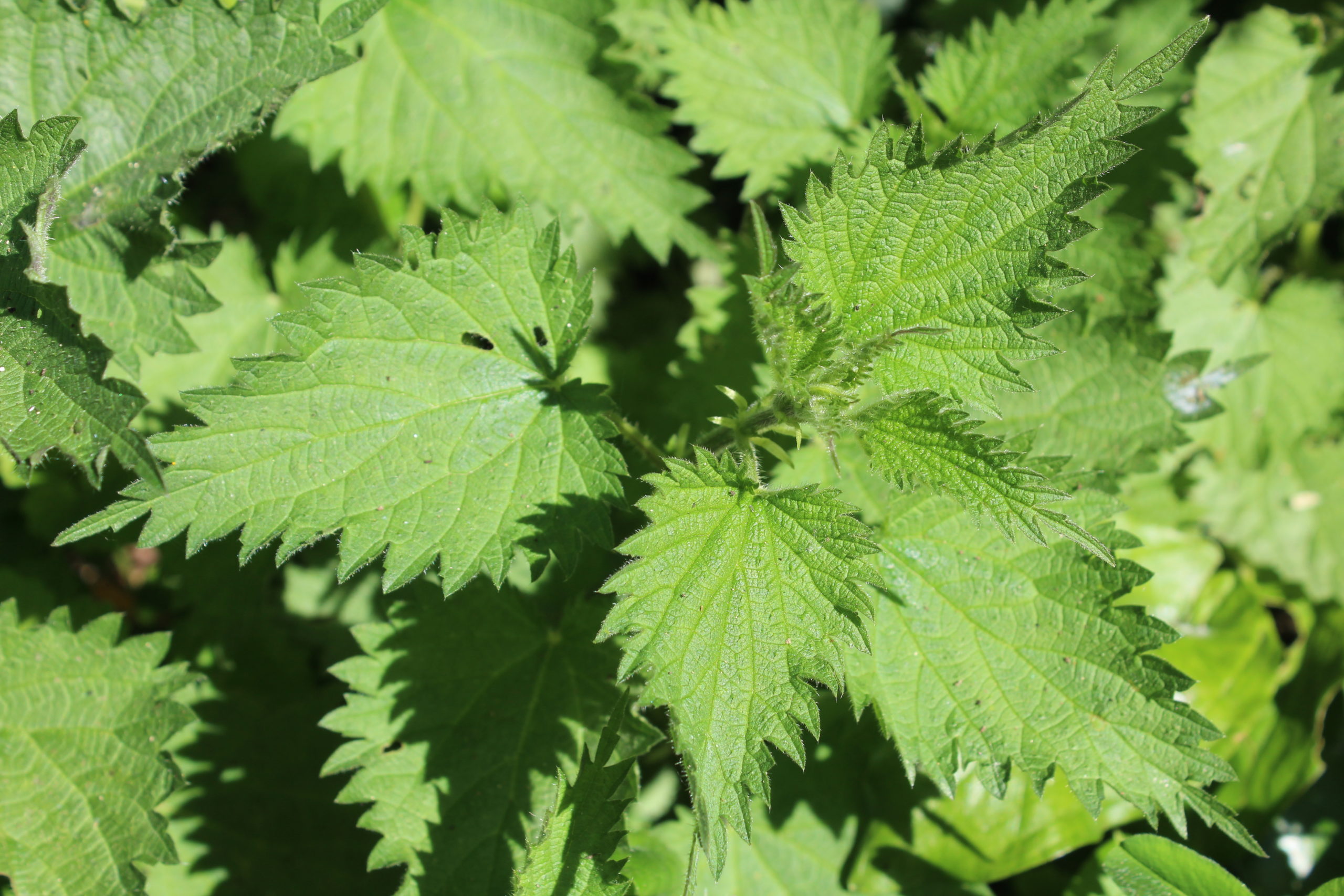
Who does not remember a painful meeting with our friends the nettles? ...
- there are many varieties (30) around the world,
- there are 5 in France,
- the most common are stinging nettle (Urtica dioica, which has the particularity of being perennial),
- and the burning nettle (Urtica urens, which is a smaller annual).
The nettle ecosystem allows us to discover a whole world and its presence allows us to learn more about our soils.
Bio-indicator plant
Reading Gérard Ducerf we learn that the most common that we will see today:
- prefers floodplain or riverside forests,
- as well as forest edges,
- that she also loves places modified by man: gardens, paths, meadows, hedgerows, orchards ...
Its presence indicates:
- regular saturation with water (especially in winter): this causes a change in the state of the iron in the soil, and it is sometimes also just a sign of the presence of "dumps" for iron objects
- too much archaic plant organic matter which characterizes a soil evolving towards a forest type soil
- too much animal organic matter: that's why it is easy to find nettles where there are horses, in rejection areas, near manure heaps ...
We will therefore easily benefit from his presence in a Paddock Paradise in equine permaculture: this is very good news.
Biodiversity reservoir plant
Insects, birds, amphibians and mammals form a rich and complex food web.
More than 40 species of insects
Butterflies :
- butterfly larvae that make their nests of silk at the top of the stems,
- butterfly that lays its egg on leaves exposed to the sun only (to find out more go see here),
- the specific nettle moth,
- the mint scale which is a moth ...
Others :
- green or black aphids which will feed the larvae of ladybugs, and the ants which raise them,
- spiders,
- weevils,
- leafhoppers that suck their sap,
- carnivorous bugs,
- mosquitoes of all kinds: what will be a concern for us with skin-rash horses (and which explains why, in general, all horses that have a choice choose other shaded areas than hedges in summer,
- grasshoppers ...
Birds
- insectivorous : blue tits, warblers and other small, agile birds that will eat aphids
- but also granivorous : sparrows, partridge, bullfinches, pheasants
- or even herbivores : like the geese who can set up their nest there ...
Batrachians
In this often very cool environment we also find frogs like the green frog ...
Mammals
- the hedgehog finds snails and slugs there,
- and the weasel finds voles there,
- obviously the fox is not far away!
- while rabbits, hinds, deer feel safe there ...
Preserving islands of biodiversity
Equine permaculture means understanding better and differently the role of the different elements of your site's ecosystems: so you better know why to protect nettles.
- to enrich animal biodiversity,
- pour protéger les biodiversité de vos cultures : un ilôt d’ortie au potager nourrit les pucerons… et protège vos plantations,
- a handful of nettle rich in nitrogen at the bottom of the tomato planting hole protects them from mildew,
- nettles mixed with the compost pile of manure are an excellent compost activator ...
You can continue your discovery of nettles here!